When it comes to the world of viticulture and winemaking, the quest for innovation and sustainability is unceasing. In recent years, a remarkable group of grape varieties has been making waves in the industry, drawing attention for their unique characteristics and environmental benefits. These varieties, known as Piwi grapes, are becoming increasingly popular among growers and wine enthusiasts alike. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the fascinating realm of Piwi grape varieties, exploring what makes them special and why they’re gaining traction.
Understanding Piwi Grapes: A New Approach to Viticulture
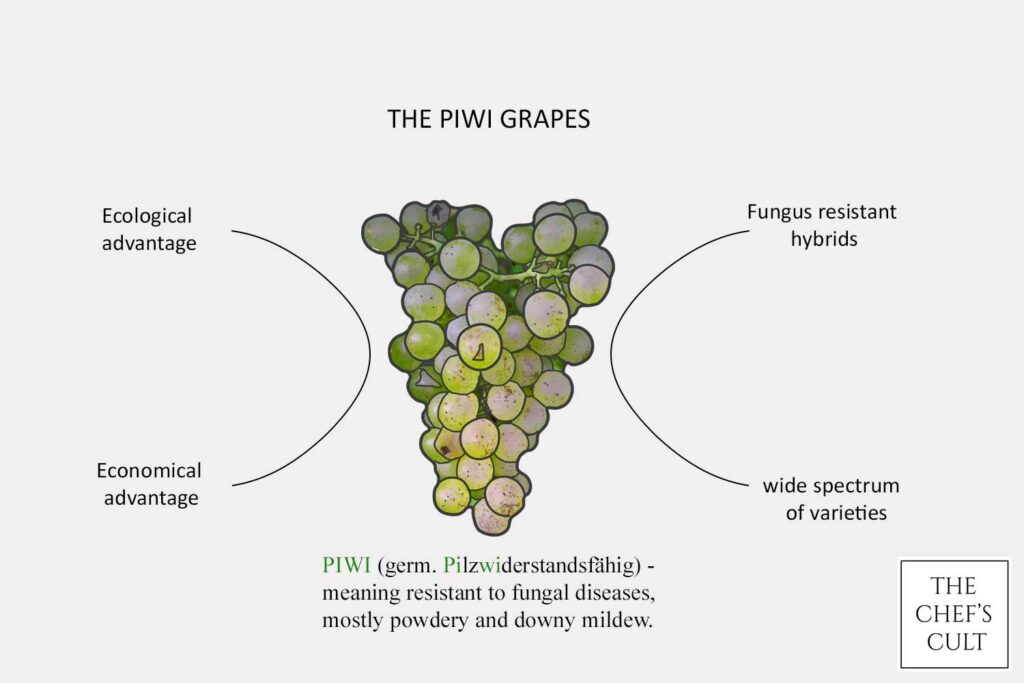
The term “Piwi” is derived from the German phrase “Pilzwiderstandsfähig,” which translates to “fungus-resistant.” Piwi grape varieties are hybrids bred to possess a natural resistance to fungal diseases like powdery mildew and downy mildew. This resistance is inherited from wild American grape species, which have co-evolved with these diseases for centuries.
Traditional grape varieties often require intensive chemical treatments to combat fungal infections, which can have detrimental effects on both the environment and the quality of the final wine. Piwi grapes, on the other hand, significantly reduce the need for such treatments, leading to a more sustainable and eco-friendly approach to viticulture.
Diversity of Piwi Varieties
One of the exciting aspects of Piwi grapes is the diverse range of flavors and aromas they bring to the world of winemaking. Just like traditional grape varieties, Piwi grapes exhibit a wide spectrum of characteristics, allowing winemakers to craft wines with unique and distinctive profiles.
Environmental Benefits and Sustainability
The ecological advantages of cultivating Piwi grape varieties cannot be overstated. The reduced need for chemical treatments not only promotes healthier ecosystems in the vineyards but also minimizes the potential for harmful residues in the final wines. This aligns with the growing consumer demand for wines that are not only delicious but also environmentally conscious.
Furthermore, the resistance of Piwi grapes to fungal diseases lessens the economic burden on grape growers. With fewer inputs required to maintain healthy vines, growers can achieve better crop yields and save on production costs.
Challenges and Considerations
While Piwi grapes offer numerous benefits, they also present some challenges for winemakers. One of the concerns is maintaining the balance between disease resistance and traditional wine quality characteristics. Some Piwi varieties might exhibit unique flavors that deviate from what consumers expect in certain wine styles. Striking the right balance between disease resistance and desirable wine attributes requires careful breeding and winemaking techniques.
The PIWI grape varieties
Solaris
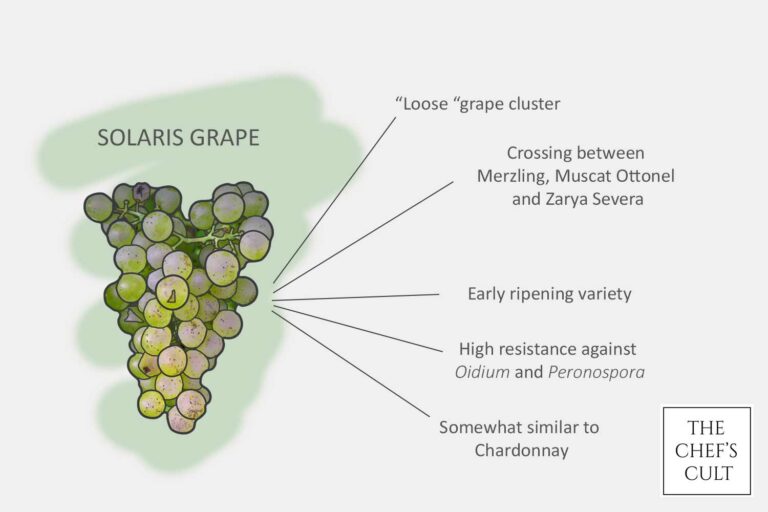
Today there is really an abundance in different PIWI grape varieties in different shapes, sizes, colors and of course, flavors. We’ll mention only the (for now) most planted ones. We’ll begin with the most well-known PIWI variety called Solaris.
Solaris is a white grape variety that was specifically developed for cool-climate viticulture. It is a hybrid grape variety, created by crossing Merzling and GM 6493 (a Seyve-Villard hybrid), and it was developed in Germany. Solaris is known for its resistance to various diseases, which makes it suitable for cultivation in regions with challenging growing conditions.
One of the key characteristics of Solaris is its early ripening, allowing it to thrive in cooler climates where other grape varieties might struggle to reach full maturity. This characteristic makes Solaris an attractive choice for vineyards in northern Europe and other regions with similar climates. The grapes are often used to produce white wines that are crisp, aromatic, and can display a range of fruity and floral notes.
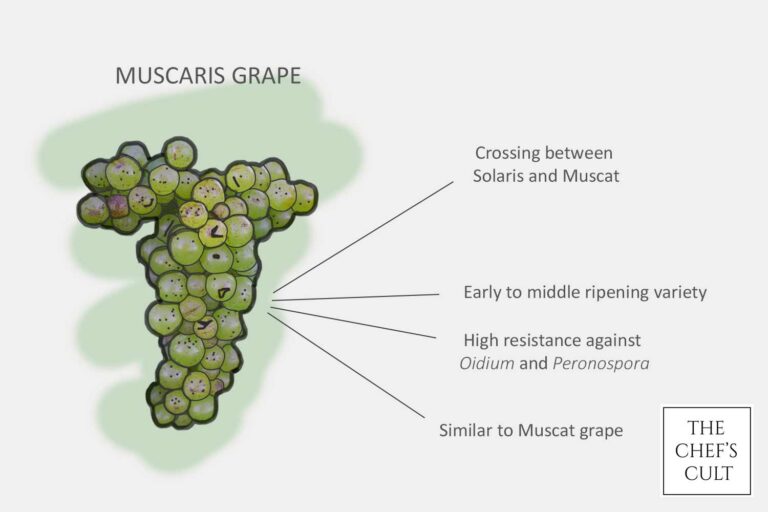
Muscaris grape
It is a cross between Solaris and a Muscat variety, resulting in a grape that combines characteristics of both parents. Muscaris was created with the goal of producing a grape variety that is well-suited for cooler climates!
Similar to Solaris, Muscaris is known for its ability to thrive in regions with challenging growing conditions. It is particularly appreciated for its resistance to fungal diseases, which can be beneficial in organic or sustainable vineyard practices. The grapes are often used to produce aromatic white wines with floral and fruity notes, and they can contribute to the production of both dry and off-dry styles of wine.
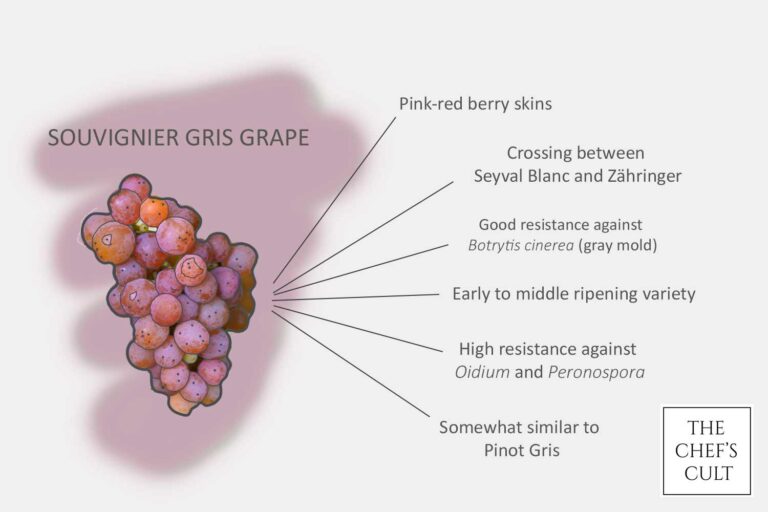
Souvignier gris grape
Souvignier gris is a relatively new grape variety originating from Germany (like many other PIWI’s are). It’s a cross between Seyval Blanc and Zähringer known for its pinkish red skin. It’s more neutral in its aromatics and flavor profile, but very similar to Pinot Gris. It is present in the German speaking countries (Germany, Switzerland and Austria). But you can find it all over the world!
The Promising Future of Piwi Grapes
As the global wine industry seeks sustainable solutions to challenges posed by disease management and environmental impact, Piwi grape varieties are poised to play an integral role in shaping the future of viticulture. Their ability to thrive without heavy chemical intervention opens up possibilities for a more harmonious coexistence between vineyards and the natural world.
Whether you’re a winemaker, a wine enthusiast, or simply someone interested in the evolution of agricultural practices, keeping an eye on the development of Piwi grape varieties is undoubtedly worth your while. These grapes are a testament to human ingenuity and our ongoing pursuit of both delicious wines and a healthier planet. So, next time you uncork a bottle of wine made from a Piwi variety, raise your glass to the marriage of tradition, innovation, and sustainability that it represents.


